The annual meeting of the European Society for Radiotherapy and Oncology (ESTRO), originally due to take place in April, is now being staged as a fully digital event

The annual meeting of the European Society for Radiotherapy and Oncology (ESTRO), originally due to take place in April in Vienna, was one of the early casualties of the Covid-19 pandemic. Postponed once to August, the event organizers decided to further delay the meeting to the end of November in the hope of convening a reduced live congress along with enhanced online participation.
However, the resurgence of coronavirus in Europe has forced another rethink, and ESTRO 2020 will now be staged as a fully digital event. The main online congress will take place from 28 November to 1 December, with attendees able to access the scientific programme via a digital platform that includes Q&A and polling functionality to enable interaction with the speaker. Several pre-congress sessions are also available online, including three short courses on a dedicated education platform, while all registered participants will be able to view all sessions on demand after the congress has finished.
The theme for this year’s event is “Translating research and partnership into optimal health”. Meeting chair Umberto Ricardi from the University of Turin, Italy, points out that technologies and methodologies in radiation oncology are evolving rapidly, but that these advances will “only truly provide impact when the new findings can be translated into clinical applications that will result in optimal benefit for each individual patient in daily practice”.
ESTRO 2020 will also host Europe’s largest industrial exhibition in radiation oncology. This year a virtual exhibition will enable attendees to interact with industry leaders and to find more about the latest innovations in technology, techniques and oncology products – a few of which are highlighted below.
Innovating and evolving radiotherapy quality assurance
Quality assurance (QA) plays a fundamental role in any radiotherapy procedure. IBA Dosimetry is working to shape QA to advance patient safety in radiation therapy, proton therapy and medical imaging. The company predicts that its latest innovations will bring the accuracy and efficiency of QA to a new level. Future solutions, meanwhile, will significantly reduce QA times and further streamline the medical physics workload.
Independent QA is essential to ensure reliable, trustworthy and accurate QA, and has been assumed as a given in the radiotherapy community. But as radiotherapy systems increasingly offer built-in “self-check” QA, the need for independent QA becomes imperative. To raise awareness of this topic, IBA Dosimetry has teamed with radiotherapy QA equipment vendors worldwide to launch an “Independent Quality Assurance” initiative.
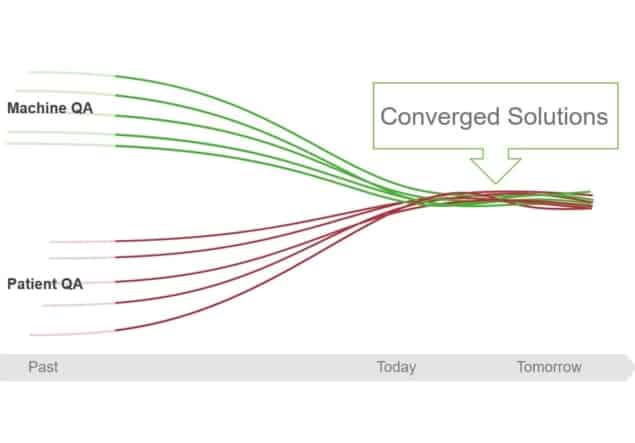
IBA Dosimetry also highlights the need for convergence of machine and patient QA. Today, QA applications for validating the treatment machine and those for verifying the patient-specific plan generally have little or no connectivity. Combining data from patient QA and machine QA will provide more precise outcomes and faster results.
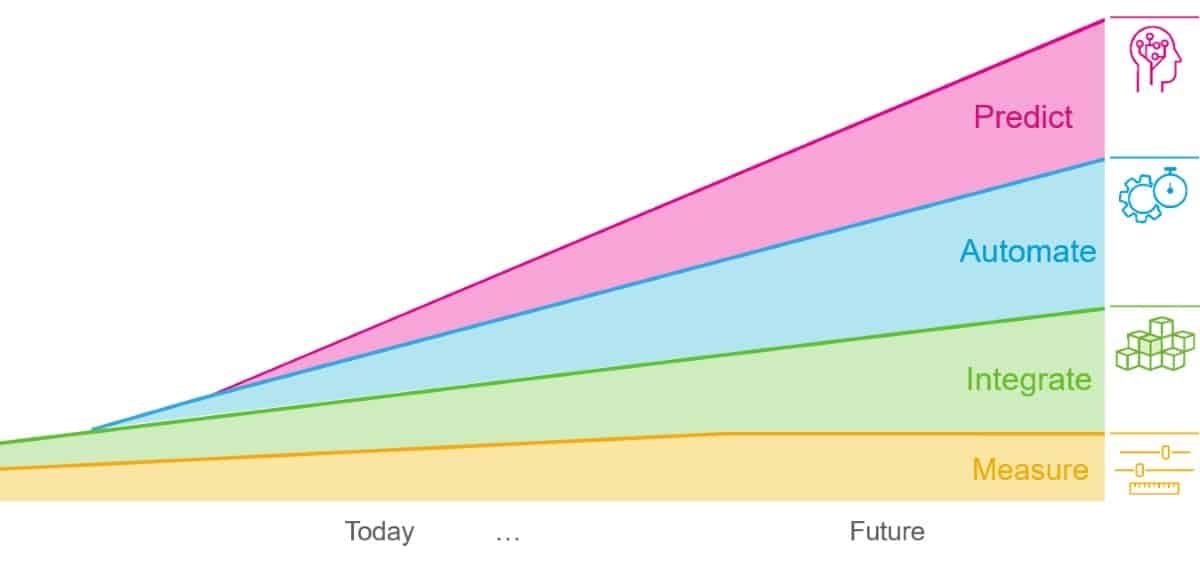
These QA innovations are based on four strategic pillars – implementation of measurements, integration, smart automation and prediction of QA results – that help save valuable time of the medical physicist and provide higher accuracy and increased confidence. IBA Dosimetry notes that while measurements will remain important for future QA, further integration, Monte Carlo-based predictive QA and automation will enable users to measure only where it really matters, leading to fewer measurements with better quality results.
Software platform standardizes treatment plan review
Peer review of treatment plans is a powerful strategy in radiation oncology clinics to ensure patient safety and plan quality, but time constraints in the daily routine can make it difficult to prepare and review patient cases in an optimal way. MIM Harmony is a dedicated software platform that provides rapid and reproducible treatment plan review, allowing medical teams to focus their efforts on a deeper, critical evaluation of patient cases and to improve the quality of their treatment plans.
MIM Harmony allows clinicians to prepare patient cases automatically, saving valuable time and ensuring that all the necessary information is available at the review meeting. Each review is guided by a disease site-specific worklist that can be fully customized to suit the needs of each clinical team, offering a flexible but standardized approach to patient care.

MIM Harmony’s customizable worklist, along with flexible task automation, reporting tools, and advanced analytics, enhance multiple peer-review formats such chart rounds, contour rounds, and one-to-one consultations. Its robust data analytics platform moves beyond traditional peer review, compiling critical information after each meeting to help identify areas for improving quality or clinical practice.
Fast and filmless patient QA now extends to multitarget treatments
Quick and convenient patient-specific quality assurance (QA) is essential for delivering stereotactic radiotherapy safely and effectively. The SRS MapCHECK from Sun Nuclear is a patient QA solution that replaces conventional film with a high-density diode array, providing accurate dose measurements in minutes rather than hours. With nearly 400 devices in clinical use and a growing body of supporting literature, the SRS MapCHECK has been proven to efficiently detect the most common sources of errors in stereotactic treatments and has become the gold standard for time-sensitive patient QA.
The system comes with SNC Patient software, which corrects for angular dependence, field size and pulse rate to ensure accurate patient QA from any angle. A new update to the software now makes it possible to simplify QA workflows for single-isocentre multiple-target (SIMT) treatments, with a new QA Setup Tool providing guidance for the optimal set-up of SIMT plans and simplified shifts for larger field sizes.
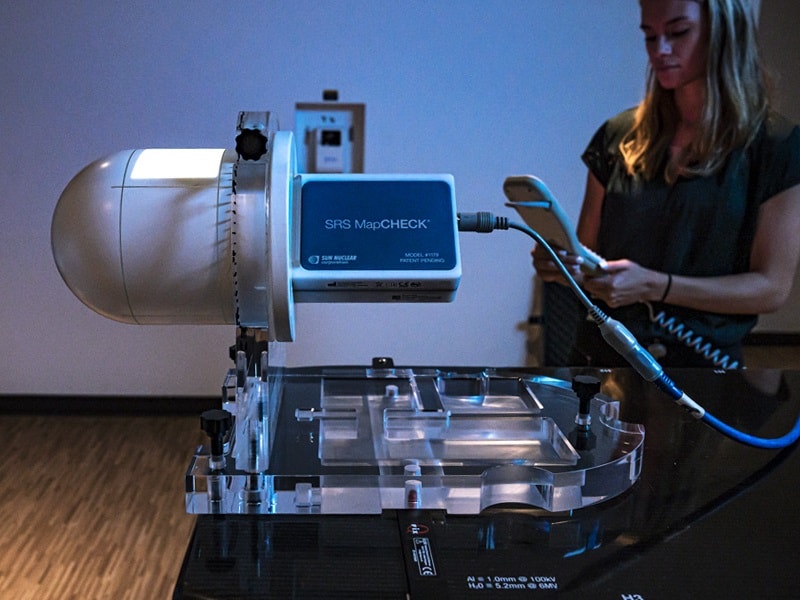
This software update, described in more detail in this short video, complements Sun Nuclear’s MultiMet-WL Cube, designed for machine QA of SIMT treatments, and adds to a suite of StereoPHAN QA solutions for stereotactic radiotherapy. During ESTRO 2020, on 30 November at 13.00 CET, Sun Nuclear will host a satellite symposium entitled “Advancing QA: Latest Solutions from Sun Nuclear”. Presentations and demonstrations will showcase both SRS MapCHECK and the SunCHECK platform.
Tracking device promises more precision for prostate cancer treatment
New radiotherapy technologies such as image guidance, high-precision dose delivery and more accurate target definition are making it possible to administer higher radiation doses in fewer treatment sessions. For prostate cancer, an improved understanding of the biological mechanisms underlying the use of hypofractionation suggests that the delivery of fewer and larger fractions has the potential to improve the therapeutic ratio while also shortening the overall treatment time.
Hypofractionated radiotherapy delivered via stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT) offers a high dose per fraction within a small number of fractions, but the steep dose gradient demands a high level of reliability during the entire treatment delivery process. At even small distances from the target the radiation dose decreases rapidly, which means that prostate motion during treatment might result in spatial misses and the exposure of surrounding healthy tissues to radiation.
The RayPilot HypoCath system from Micropos Medical is a removable electromagnetic transponder that offers real-time tracking of the tumour throughout the treatment process. The electromagnetic tracking device is compatible with conventional linacs and requires no surgical intervention, with the transmitter integrated into a standard urinary catheter to enable localization of both the prostate and the urethra.
The system has already been trialled at the Ospedale San Gererdo in Monza, Italy, with the results reported in a recent white paper by Professor Stefano Arcangeli. Tests with four patients showed that the electromagnetic tracking device kept the average target motion within 2 mm throughout treatment delivery, with no impact on patient comfort. Arcangeli notes that further improvements in the accuracy could be achieved by fine tuning the workflow, which he believes would make SBRT well positioned to become the procedure of choice for patients with localized prostate cancer.
Upgraded software enhances daily testing regime
Quality assurance (QA) in radiation treatment planning is becoming ever more important as medical physicists seek to optimize image-guided radiotherapy (IGRT) protocols for the delivery of higher doses and emerging adaptive treatments. Imaging phantoms are essential to calibrate and commission IGRT systems on a daily basis, and the QUASAR Penta-Guide Phantom from Modus QA has become recognized globally as the preferred tool for efficient daily testing of key parameters such as system alignment and imaging performance.
Modus QA is now enhancing the capabilities of this phantom with the new Penta-Guide 2.0 software, a comprehensive daily QA solution that is free for all existing and new Penta-Guide users. Designed to improve the daily QA workflow, the software offers advanced features such as automated monitoring of system alignment, image quality analysis, and improved reporting and visualization tools.

An online presentation by product manager Rocco Flores will highlight the innovative features of the Penta-Guide phantom, review the daily QA user workflow, and explain the advanced utility of the Penta-Guide 2.0 software.